Discover the fascinating world of yarn manufacturing as we unravel the various processes involved in transforming fibers into versatile and vibrant threads.
Welcome to my blog, where we’ll be exploring the fascinating world of yarn manufacturing processes. Yarn is an essential material for knitting and crocheting enthusiasts, and understanding the different types of yarn manufacturing processes can help you choose the perfect yarn for your next project.
From traditional methods that have been used for centuries to modern techniques that use cutting-edge technology, there are many ways to produce high-quality yarn. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at some of the most common types of yarn manufacturing processes and explore their unique characteristics.
So grab a cup of tea or coffee and let’s dive into the wonderful world of yarn!
Introduction to Yarn Manufacturing
Yarn manufacturing is a complex process that involves several stages, from the selection of raw materials to the final product. The process begins with selecting high-quality fibers such as cotton, wool, silk or synthetic fibers like polyester and nylon.
These fibers are then processed through various machines and techniques to create yarns of different thicknesses and textures.
The history of yarn manufacturing dates back centuries when people used hand-spun threads for weaving fabrics. With time, technology has advanced significantly in this field leading to modern methods that use sophisticated machinery for producing high-quality yarns.
Today’s textile industry relies heavily on automated processes which have made it possible to produce large quantities of quality yarn at an affordable cost. However, despite these advancements in technology there is still a need for skilled workers who can operate these machines effectively while maintaining quality control standards throughout the production cycle.
Background and History

The earliest evidence of yarn production can be traced back to the Middle East and Egypt, where people used spindle whorls and drop spindles to spin fibers into thread. In medieval Europe, spinning wheels were introduced, which made it easier for people to produce yarn in larger quantities.
During the Industrial Revolution in the 18th century, new technologies such as water-powered mills and steam engines revolutionized yarn manufacturing processes. This led to mass production of high-quality yarns at lower costs than ever before.
Today’s modern technology has further improved upon these methods with computer-controlled machines that can produce consistent quality threads at an even faster rate than before.
Raw Materials for Yarn Manufacturing
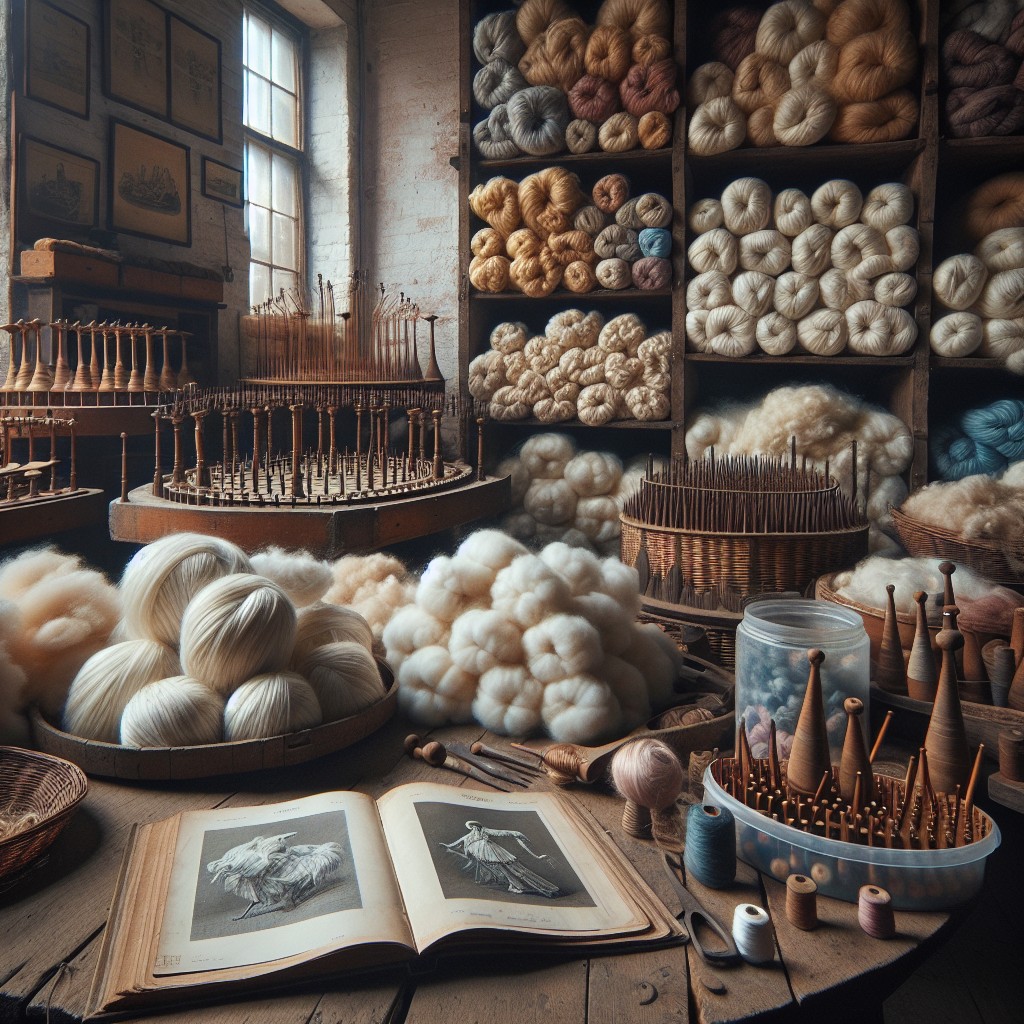

Yarn can be made from a variety of fibers, including natural and synthetic materials. Natural fibers include cotton, wool, silk, linen and hemp while synthetic fibers include polyester and nylon.
The quality of the final product depends on several factors such as fiber length or staple length which is measured in inches or centimeters; fineness which refers to diameter; strength measured by tensile strength tests; elasticity determined by how much stretch a fiber has before breaking among others.
Different types of yarn require different raw materials depending on their intended use. For example, cotton is commonly used for making lightweight summer garments because it’s breathable while wool is ideal for winter clothing due to its insulating properties.
In addition to choosing the right type of fiber for your project needs you also need consider other factors like color fastness (how well colors hold up over time), texture (smooth vs rough) and durability when selecting your raw material.
Ginning Process
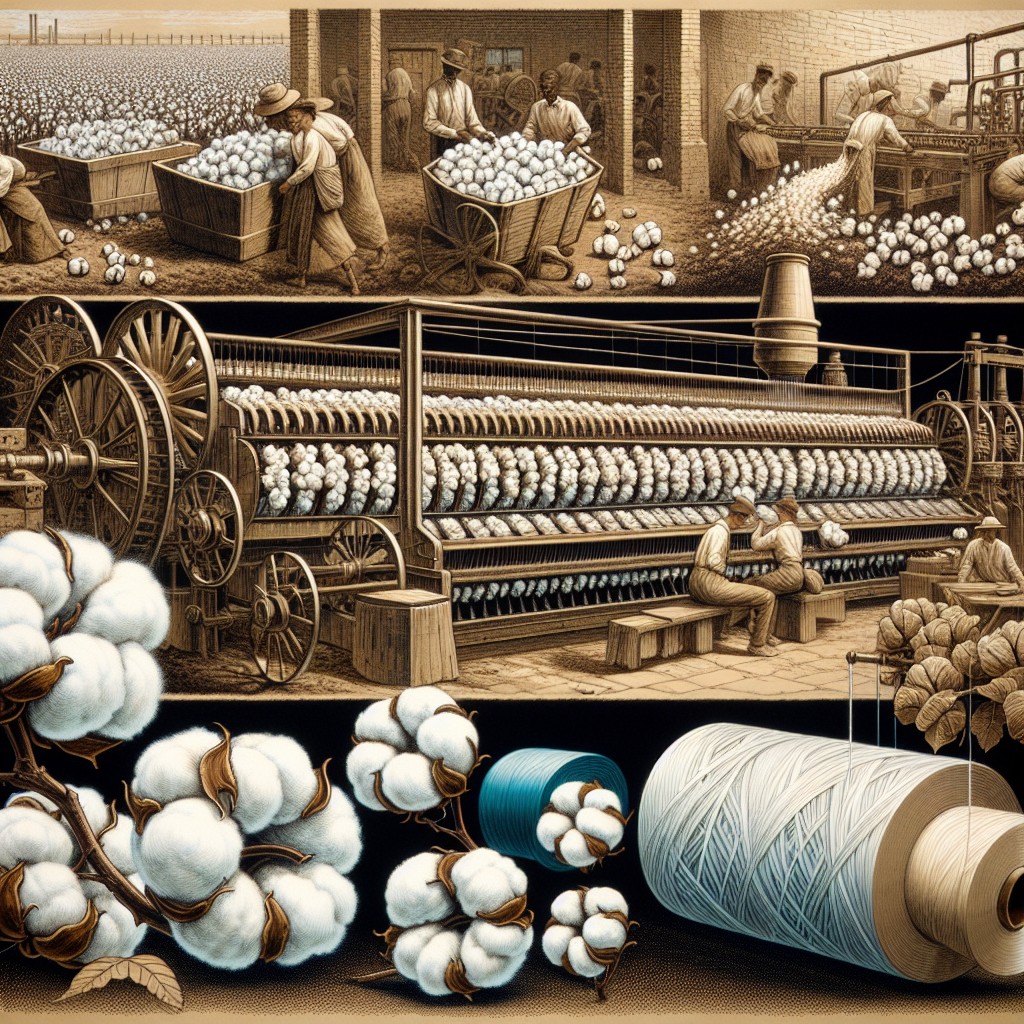

This process is crucial because it determines the quality of the final product. The cotton bales are opened, and then they go through a machine called a gin that separates the seeds from the fiber.
After this stage, we have raw cotton that can be used for further processing.
Ginning has come a long way since its invention in 1793 by Eli Whitney when he invented his famous Cotton Gin machine to automate this labor-intensive task. Today’s modern gins use advanced technology to increase efficiency while reducing waste.
Blow Room Operations

The primary objective of this stage is to remove impurities and prepare the fibers for carding. Blow room operations involve several steps, including opening and cleaning, mixing and blending.
During opening and cleaning, machines called scutchers or beaters are used to separate clumps of cotton fiber into individual strands. This process also removes dirt particles that may have been missed during ginning.
The next step in blow room operations is mixing and blending. Here different batches of cotton with varying properties such as color or staple length are mixed together in a predetermined ratio using automated systems like hopper feeders or pneumatic conveyors.
Opening and Cleaning
This process involves separating and removing impurities from cotton fibers to ensure that only high-quality materials are used for spinning. The opening machine uses spiked rollers to open up compressed bales of cotton, while a series of fans blow away any dust or debris.
Once opened, the fibers move on to a cleaning machine where they undergo further processing. Here, metal detectors remove any metallic objects that may have been accidentally mixed with the cotton during transportation or storage.
The cleaned fibers then pass through another set of machines called carding machines which aligns them into thin sheets known as “webs.” These webs are then fed into drawing frames where they undergo several processes such as drafting and doubling before being spun into yarn using ring spinning method.
Opening and cleaning is an essential part of yarn manufacturing because it ensures that only high-quality raw materials are used for making threads.
Mixing and Blending
The goal of mixing is to create a uniform blend of fibers that will produce consistent yarn quality. Blending, on the other hand, involves combining different types of fibers to achieve specific characteristics such as strength, softness or color.
In modern yarn manufacturing processes, computer-controlled machines are used for mixing and blending operations. These machines can handle large volumes of fiber blends with precision and accuracy.
The most common method used for mixing is called “batch processing.” In this method, a predetermined amount of each type of fiber is weighed out according to the desired blend ratio. The fibers are then mixed together using mechanical agitation until they form a homogeneous mixture.
Blending involves combining two or more different types or colors of fibers into one cohesive unit before spinning them into yarns. This process allows manufacturers to create unique textures and colors that cannot be achieved by using single-fiber materials alone.
Carding Process
This process involves separating and aligning fibers to create a continuous web or sliver of fiber that can be spun into yarn. The carding machine uses wire teeth to comb through the fibers, removing any remaining impurities and straightening them out.
The resulting web of fiber is then condensed into a thin rope-like structure called a sliver. The thickness of this sliver determines how thick or thin the final yarn will be.
Carded woolen yarns are typically thicker than combed worsted ones because they contain more air pockets between fibers due to less alignment during processing.
Comber Process
This process involves the use of a machine called a comber, which removes any remaining short fibers and impurities from the cotton fibers. The result is long and uniform cotton sliver that can be spun into strong and smooth yarn.
During the comber process, several machines are used to prepare the fiber for spinning. First, after carding comes combing where finer brushes remove shorter fibres leaving only longer ones behind; this results in an even more refined product than before! Then drawing frames stretch out these fibres so they’re all roughly equal length before being twisted together on spindles or bobbins – creating thread ready for weaving or knitting projects.
Understanding how each stage of yarn manufacturing works can help you appreciate why certain types of yarn are better suited for specific projects than others.
Drawing in Yarn Manufacturing
The primary objective of drawing is to produce uniformity in the fiber bundle, which results in consistent yarn quality. Drawing machines are designed to pull out fibers from several carded slivers and combine them into one strand, which is then fed through rollers that stretch it further.
The number of drawing stages varies depending on the desired final product specifications. For instance, fine cotton or silk threads may require up to eight stages while coarser woolen threads may only need two or three stages.
During each stage, drafting rollers rotate at different speeds creating tension between them as they draw out fibers from multiple strands simultaneously. This action aligns individual fibers parallelly resulting in a more even distribution across the entire strand.
Drawing plays an essential role in producing high-quality yarn by ensuring consistency throughout production processes.
Ring Spinning Method
This process involves feeding fibers through a series of rollers and then twisting them into a continuous strand using a spindle and ring. The resulting yarn is strong, smooth, and consistent in thickness.
The ring spinning method has been around for centuries but has undergone significant improvements over time to increase efficiency and productivity. Today’s modern machines can produce high-quality yarn at an impressive rate.
One advantage of the ring spinning method is that it allows for greater control over the twist level, which affects how tightly or loosely wound the final product will be. This makes it possible to create different types of yarn with varying characteristics such as softness or durability.
Another benefit of this technique is that it produces less waste than other methods like open-end spinning since there are fewer broken fibers during production.
Cone Winding
The cone winding machine winds the yarn onto a cone, which makes it easier to handle and transport. Cones are also used for weaving and knitting machines, where they can be easily mounted on spindles or creels.
The cone winding process requires precision and accuracy to ensure that the resulting cones have consistent tension throughout their length. This is important because uneven tension can cause problems during subsequent processes such as warping or knitting.
Modern cone-winding machines use electronic sensors to monitor thread tension, speed, and other parameters automatically. They also have features like automatic doffing of full cones and splicing of broken threads without stopping production.
Twisting and Spinning
After the fibers have been cleaned, carded, combed, and drawn into thin strands of roving or sliver, they are ready to be spun into yarn. The twisting process involves taking these strands of fiber and twisting them together to create a single strand of yarn.
There are several methods for spinning yarn depending on the desired outcome. One popular method is ring spinning where a machine twists fibers around a bobbin using rings that guide it through each stage until it becomes tightly twisted enough to hold its shape as one continuous thread.
Another method is open-end or rotor spinning which uses air pressure instead of rings to twist fibers together quickly at high speeds resulting in bulkier but less durable threads.
Once spun into individual skeins or cones, quality control measures ensure that each batch meets specific standards before being shipped out for use by knitters and crocheters worldwide.
Quality Control in Manufacturing
It ensures that the final product meets the required standards and specifications. Quality control in yarn manufacturing involves several stages, including raw material inspection, process monitoring, and finished product testing.
Raw material inspection involves checking for defects such as contamination or damage to fibers before they are processed into yarn. Process monitoring includes regular checks on machinery performance to ensure consistent quality throughout production.
Finished product testing is done after the spinning process to check for strength, durability, colorfastness and other characteristics that determine its suitability for different applications like knitting or weaving.
Yarn manufacturers use various tools such as spectrophotometers (to measure color), tensile testers (to test strength) among others during quality control processes.
The Future of Yarn Manufacturing
New methods and techniques are being developed that promise to make the process more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly. One such innovation is air-jet spinning which uses compressed air instead of a spindle to twist fibers into yarn.
This method reduces energy consumption by up to 50% compared with traditional ring spinning.
Another exciting development is the use of nanotechnology in textile production. Nanofibers can be produced using electrospinning or meltblowing processes that create ultra-fine fibers with diameters as small as one-thousandth of a human hair’s width! These nanofibers have unique properties such as high strength-to-weight ratio, increased surface area for better absorption or filtration capabilities.
In addition to these technological advancements, there is also growing interest in sustainable practices within the industry. Many manufacturers are exploring ways they can reduce their carbon footprint by using renewable energy sources like wind or solar power and implementing recycling programs for waste materials.
Conclusion On Yarn Manufacturing Processes
From the selection of raw materials to the final product, each step requires precision and attention to detail. The quality of yarn depends on various factors such as fiber type, spinning method, twist level, and finishing processes.
As technology advances in this field so does the efficiency of production methods which leads to better quality products at lower costs.
Understanding these different types of yarn manufacturing processes can help you choose high-quality threads for your next project while also appreciating how much work goes into producing them.
Training and Education in Yarn Manufacturing
To become an expert in this field, you need to undergo extensive training and education. Many universities, colleges, technical schools, and vocational institutions offer courses on yarn manufacturing processes.
These programs cover various aspects of yarn production such as fiber selection, blending techniques, spinning methods as well as quality control measures. They also provide hands-on experience with the latest equipment used in the industry.
In addition to formal education programs offered by academic institutions or trade organizations like The Textile Institute (TI), there are many online resources available for those who want to learn more about yarn manufacturing processes at their own pace.
Relevant Books and Periodicals
Some of the most popular titles include “The Art of Yarn Manufacturing,” “Handbook of Textile Design: Principles, Processes, and Practice,” and “Yarn Production: Science Technology & Economics.” These resources cover a wide range of topics related to yarn manufacturing processes, from the history and background to modern techniques used today. There are several industry-specific magazines such as Spin-Off Magazine or Knitting Industry News that offer regular updates on new developments in yarn production technology.
Useful Resources and Apps for Learning
Some of the best resources include online courses, instructional videos, and books on the subject. You can also find a wealth of information on websites dedicated to knitting and crocheting communities.
One app that stands out is “YarnBuddy,” which provides users with access to a vast library of patterns for various projects such as hats, scarves or blankets. The app also features tutorials on different types of stitches used in crochet or knitting.
Another great resource is “Craftsy,” an online platform that offers classes taught by experts in their respective fields. They have several courses related to yarn manufacturing processes like spinning wool into yarn using hand spindles or drop spindles.
If you prefer reading books over watching videos or taking classes online then check out some popular titles like “The Spinner’s Book Of Yarn Designs” by Sarah Anderson which covers everything from fiber preparation techniques through plying methods; Or “The Intentional Spinner” by Judith MacKenzie McCuin who shares her expertise about how different fibers behave during processing stages while providing tips for achieving desired results when spinning them into yarns.
With these resources at your fingertips along with our article outlining the most common types of yarn manufacturing processes – it won’t be long before you become an expert yourself!.
FAQ
What is the process of making yarn called?
The process of making yarn from the fibre is called spinning, which involves drawing out and twisting fibres from a mass of cotton or wool to form yarn.
What are the two main process of making yarn?
The two main processes of making yarn are weaving and knitting.
What are the 3 major yarn categories?
The 3 major yarn categories are Animal Fibers, Plant Fibers, and Synthetic Fibers.
What is the process of yarn in textile?
The process of yarn in textile involves spinning, where extracted fibers are twisted together to form yarn and passed through multiple sets of rotating rollers at successively higher speeds.
How do natural and synthetic fibers differ in the yarn manufacturing process?
Natural and synthetic fibers differ in the yarn manufacturing process, as natural fibers like cotton, wool, or silk are derived from plants and animals, while synthetic fibers like polyester or nylon are produced with petroleum-based chemicals.
What role does technology play in modern yarn production methods?
Technology plays a crucial role in modern yarn production methods by enabling automation, improving consistency and quality, and increasing the efficiency of the overall manufacturing process.
How do various yarn manufacturing processes impact the characteristics and quality of the final product?
Various yarn manufacturing processes impact the characteristics and quality of the final product by influencing fiber alignment, tensile strength, appearance, and texture.





